GOUT
The name gout comes from the Latin word Gutta which means "a drop", because of an ancient belief that the disease was due to noxa (injurious agent, act, or influence) falling drop by drop into the joint. It has now come to be known as a group of disorders of purine metabolism, manifested by various combinations of hyperuricemia (elevated urica acid in the blood), recurrent acute inflammatory arthritis induced by crystals of monosodium urate monohydrate, tophaceous deposits of these crystals in and around the joints of the extremities (which may lead to crippling destruction of joints), and uric acid urolithiasis (kidney stones).
Gout is a metabolic disorder associated with abnormal amounts of urates in the body that is due to the overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid....sometimes both. It is especially common in Pacific islanders (Filipinos and Samoans for example). A secondary cause of gout is related to acquired causes of hyperuricemia. Examples are: medication use (especially diuretics, cyclosporine, low-dose aspirin, and niacin), myeloproliferative disorders, multiple myeloma, hemoglobinopathies, chronic renal disease, hypothyroidism, psoriasis, sarcoidosis, and lead poisoning. Alcohol ingestion in any form promotes hyperuricemia by increasing urate production and decreasing the renal excretion of uric acid.
Most gout victims are male. In fact nearly 90% of people who suffer from gout are men over the age of thirty. But women are not immune, particularly if they are taking medications such as those for hypertension and hormone replacement which can predispose them to the condition, or have passed menopause.
Some Possible Causes of Elevated Uric Acid Levels
Medication- Diuretics used for weight loss or heart disease, insulin, some antibiotics, medication for rheumatoid arthritis, or an overdose of pharmaceutical niacin can cause uric acid levels to rise. Diuretics reduce sodium, magnesium, calcium and potassium (among other things) levels. It has also been found that certain patients taking beta blocker for high blood pressure have a related occurance of gout attacks.
Poor Kidney Function- When kidneys are not functioning at optimum levels, they lose their ability to excrete uric acid from the body. When alcohol is metabolized, lactic acid is produced, which hinders uric acid excretion by the kidneys.
Dieting-Severe dieting or fasting can cause excess lactic acid, which hinders uric acid excretion by the kidneys. Crash and severe calorie restriction diets shock your metabolism and can trigger a gout attack. Dieting may also cause a loss of potassium, which can increase urate levels in the blood.
Diet- Traditional thinking tells us that gout is the result of excessive amounts of alcohol, animal protein, heavy foods, coffee, and soft drinks in your diet. Other foods that increase uric acid are anchovies, asparagus, legumes, mushrooms, meat, organs, and shellfish. Reduction in consumption of these foods is very often successful in reducing or eliminating gout. These foods that contain high levels of purine can cause uric acid levels to rise and overburdon the processes that convert purines and eliminate uric acids. Purine is a protein substance that is transformed into uric acid during digestion. Reduction in consumption of these foods is very often successful in reducing or eliminating gout. Food allergies may lead to gout. When people who are sensitive to certain foods eliminate them from their diet they often find that their gout goes away. Gout is also more common in overweight people. Nearly half of the people with gout are at least 15% above their recommended weight. As mentioned below, dieting can trigger gout attacks.
Other Odd Causes of Gout
Stress (raises uric acid levels), surgery, Candida (yeast infection), vitamin deficiency (especially B5, A and E), chemotherapy (uric acid is released in extreme amounts due to the cellular destruction), drop in barometric pressure may trigger an attack, may all lead to gout.
Lead poisoning may be another possible cause. Lead poisoning makes the aldosterone system insensitive to potassium concentration. Aldosterone is a hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex (part of the adrenal gland) that is important in the control of blood pressure and the regulation of sodium and potassium concentration. A potassium deficiency can increase urate levels in the blood. It would be very interesting to know how many people with gout have high blood pressure.
Uric Acid Crystals
When uric acid is formed is takes the shape like that of a needle. When it takes this shape it is like it jabs its way into the joints. Uric acid is more likely to crystallize at lower temperatures, which explains why nearly 90% of gout attacks affect cooler extremities, like the big toe. This can idea can also explain why gout is seen in a disorder like hypothyroidism, where the body's thermostat is turned down.
It should be noted that uric acid is not functionally a harmful substance. It is actually a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative damage. It is considered almost as effective as vitamin C. It is only when the levels of uric acid become abnormally high that it becomes problematic.
Degowin's Diagnostic Examination manual states that early gout presents with a history of several similar episodes. Frequently, the patient is awakened by mild burning, tingling, numbness, or warmth in a joint. The site rapidly swells and becomes excruciatingly tender, even intolerant of the pressure of the bedclothes. Typically, the overlying skin becomes red or violaceous (having a purple color). There may be malaise, headache, fever, and tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
Untreated, the attack lasts for 1 or 2 weeks. In over half the cases, the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe is affected. Other sites are the instep, ankle, heel, elbow, or hand. Bilateral or migratory joint involvement sometimes occurs, which excludes the diagnosis of cellulitis, fracture, and suppurative arthritis. The attacks may be triggered by trauma, surgical operation, exposure to cold, changes in atmospheric pressure, acute infections, overindulgence in food or alcoholic beverages, the injection of foreign proteins (as in vaccines), the administation of diuretics, antihyperuricemic drugs, antileukemic drugs, epinephrine, or ergotamines.
In tophaceous gout, the clinical signs of inflammation are variable, from mild to moderately severe. After years of episodes of acute gouty arthritis, crystals of sodium urate are deposited in the tissues as gouty tophi. In the joints, they erode bone. Acting as foreign bodies, the crystals stimulate low-grade inflammation processes that may extrude the tophi through the skin in sinuses. The masses of urates and cartilaginous degeneration impair function of joints, often with asymmetric nodular swellings.
Pseudogout (false gout) is a calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, particularly in acute and subacute forms. Chondrocalcinosis is the presence of calcium salts, especially calcium pyrophosphate, in the cartilaginous structures of one or more joints. Chondrocalcinosis is commonly associated with a wide variety of metabolic disorders such as: hemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidism, ochronosis, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, Wilson's disease, and true gout.
Pseudogout is a disorder that presents to the clinician as an acute arthritis having a similarity to true gout. It is most often seen in persons age 60 or older. It is characterized by acute, recurrent and rarely chronic arthritis that usually involves large joints (most commonly in the knees and wrists) and is almost always accompanied by chondrocalcinosis of the affected joints.
Often the patient has had multiple episodes and the attack begins abruptly with painful swelling and heat. The symptoms and signs are intense for 2 to 4 days, then they gradually subside during the next 2 weeks. Fever often accompanies the inflammation (100o to 103o F). Identification of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joint asparations are diagnostic of pseudogout. Apparently, the deposition of crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate withing the joint triggers the inflammation. This cause of the deposition is unclear because the concentration of calcium is normal is tissues and serum. Also, unlike gout, pseudogout is usually associated with normal serum urate levels.
As stated, gout is a disorder of purine metabolism. A purine is a nitrogen containing compound that is not found free in nature, but is variously substituted to produce a group of compounds known as purines or purine bases. The purine bases include adenine and guanine, which are constituents of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), and hypoxanthine and xanthine. These four products are the sources of the metabolic end product called uric acid.
Figure 1 below shows what a molecule of uric acid looks like.
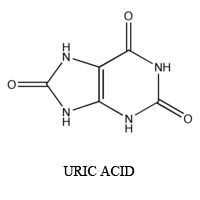
FIGURE 1
Purines can be generated by the body itself (via the breakdown of cells in normal cellular turnover) or can be ingested in purine-rich foods (e.g. meat, seafood, beer). Figure 2 shows the basic fate of ingested purines (The purine content of food reflects its nucleoprotein content. In the diagram it is shown as DNA and RNA). Degradation of dietary nucleic acids in the small intestings starts with ribonucleases and deoxyribonucleases. These are secreted in pancreatic juice and hydrolized the RNA and DNA to oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides are further hydrolized by pancreatic phosphodiesterases which break down to form mononucleotides. Another enzyme in the nucleotidase family removes the phosphate groups which releases nucleosides that can then be absorbed by the intestinal mucosal cells or can be further degraded to free bases before uptake.
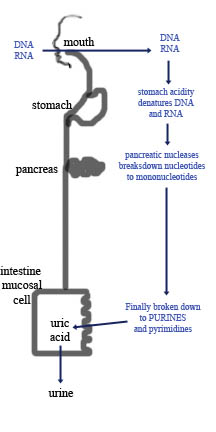
Figure 2
As seen in Figure 3, Uric acid is produced when purines are broken down by enzymes in the liver. The purines are shown with a red asterisk.
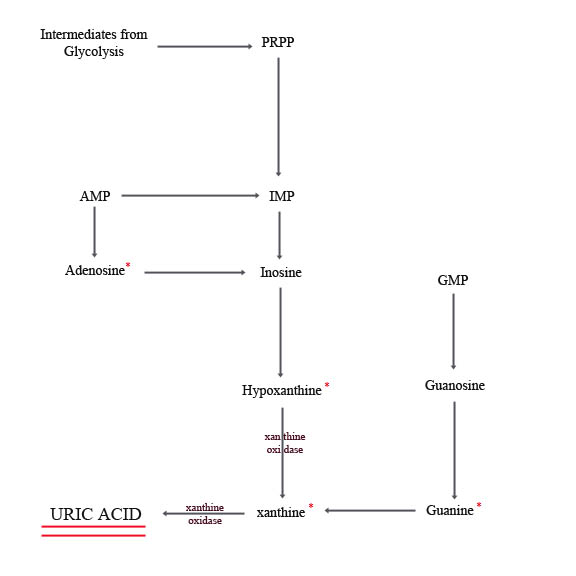
Figure 3
Seen above in Figure 3 is the formation of uric acid. A brief summary of the steps in the production of uric acid are as follows:
1. An amino group is removed from AMP to produce IMP, or from adenosine to produce inosine.
2. IMP and GMP are converted into their nucleoside forms (inosine and guanosine) by an enzyme called 5'-nucleotidase.
3. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase converts inosine and guanosine into their respective purine bases, hypoxanthine and guanine.
4. Guanine is deaminated to form xanthine.
5. Hypoxanthine is oxidized by xanthine oxidase (treatments with the drug allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase, resulting in the build up of hypoxanthine and xanthine which are more soluble than uric acid) to xanthine, which is again oxidized by xanthine oxidase to uric acid.
The kidney is responsible for about one third of uric acid excretion, with the gut responsible for the rest.
The amount of uric acid within the body is determined by the balance between the amount being produced (and ingested) and the amount being excreted.
Traditional treatment is high doses of NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or indomethacin to kill the pain, anti-inflammatories, and drugs, such as allopurinol, that inhibit formation of uric acid. Allopurinol (Zyloprim) has some serious side effects, such as skin eruptions, liver toxicity, inflammation of the blood vessels, and possible weakening of kidney function by forcing the kidneys to work too hard to excrete the uric acid. If you have kidney problems and use this drug, be sure to be carefully monitored. Another drug that is used is colchicine, but it, too, has serious side effects, including numbness in the hands and feet, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weakness, hair loss, and abnormal bleeding or bruising. Corticosteroids are used for acute attacks, but should not be used for extended periods. In my opinion, they should never be used.
To lower uric acid:
Cherries have been shown to reduce uric acid (tart cherries or tart cherry concentrate)
Strawberries or blueberries (and other dark red/blue berries) are also reputed to be beneficial
Celery extracts (celery or celery seed either in capsule form or as a tea) is believed by many to reduce uric acid levels (although these are also diuretics).
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) The vinegar changes the blood pH so that the crystals will go into solution and be excreted. Mix two teaspoons each of apple cider vinegar and raw honey in a glass of water and drink at mealtime.
Nutrients
Essential Fatty Acids- Needed to repair tissues, aid in healing, and restore proper fatty acid balance. An excess of saturated fats is often behind this disorder. Fish oil Take 2 grams of fish oil capsules 2x a day to reduce the chances of gouty inflammation
Proteolytic Enzymes- Taking with meals improves digestion of protein; taking between meals reduces inflammation. Bromelain 500 mg twice daily as an anti-inflammatory
Vitamin B complex- Needed for proper digestion and all bodily enzyme systems. B complex One to three 50 mg tablets of the complete B complex daily, plus 500 mg of pantothenic acid (B5) in divided doses to assist the body's conversion of uric acid into harmless compounds.
Vitamin C with Bioflavonoids- Lowers serum uric acid levels.
Vitamin E- improves circulation. Low-purine diets are low in vitamin E and fried foods deplete it, so supplementation will be necessary as a deficiency can contribute to the formation of excess uric acid. Begin with 100 IU of natural vitamin E, and slowly increase to 6-800 IU daily
Free-Form Amino Acid Complex (high quality protein powders)- Uric acid production increases if essential amino acids are lacking. Use a supplement containing all the essential amino acids.
Zinc- Important in protein metabolism and tissue repair.
Sea Cucumber- Marine animals that have been used as an arthritis treatment in China for thousands of years.
Supplements
L-glutamine -500 mg four times daily on an empty stomach - is an antacid.
L-glutathione -500 mg twice daily on an empty stomach - increases renal cleansing of uric acid.
L-glycine -500 mg four times daily between meals - acts as an antacid.
L-methionine -250 mg twice daily on an empty stomach - detoxifies purines.
Magnesium citrate -400 mg three times a day - an anti-spasmodic to relieve pain.
Herbs
Alfalfa is a good source of minerals and other nutrients that help to reduce serum uric acid. Take 2,000 to 3,000 milligrams daily in tablet or capsule form.
Bilberry extract is a good source of anthocyanidins and proanthocyanidins - powerful antioxidant compounds.
Boswellia and TURMERIC (curcumin) have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Cayenne (capsicum) powder, mixed with enough wintergreen oil to make a paste, to affected areas to relieve inflammation and pain. This may cause a stinging sensation at first, but with repeated use, pain should diminish markedly. Cayenne can also be taken in capsule or liquid form.
Celery seed extract contains numerous anti-inflammatory compounds.
Try using chamomile, lady's mantle (yarrow), peppermint, or skullcap, in either capsule or tea form.
Devil's claw and yucca can aid in relieving pain.
Ginger and turmeric are both anti-inflammatory and help to ease pain and swelling.
Recommendations
When an attack of gout strikes, eat only raw fruits and vegetables for two weeks. Juices are best. Frozen or fresh cherry juice is excellent. Also drink celery juice diluted with distilled water - use distilled water only, not tap water. Blueberries, cherries, and strawberries neutralize uric acid and have antioxidant properties, so eat lots of them. Also include grains, seeds, and nuts in your diet.
Maintain a diet low in purines at all times. Purines are organic compounds that contribute to uric acid formations. Purine-rich fods to avoid include anchovies, mackerel, shellfish, asparagus, consomme, herring, meat gravies and broth, mushrooms, mussels, sardines, peanuts, baker's and brewer's yeast, mincemeat, and sweetbreads. Thyme and thyroid extracts can also pose a problem if taken for long periods of time.
Enjoy foods like rice, millet, starchy vegetables, green vegetables, corn, cornbread, fruit, eggs, and nuts.
Consume plenty of quality water. Fluid intake promotes the excretion of uric acid.
Eat no meat of any kind, including organ meats. Meat contains extremely high amounts of uric acid.
Consume no alcohol. Alcohol both increases the production of uric acid and reduces uric acid elimination. Beer and wine also contain yeast.
Do NOT eat any fried foods, roasted nuts, or any other foods containing (or cooked with) oil that has been subjected to heat. When heated, oild become rancid. Rancid fats quickly destroy vitamin E, resulting in the release of increased anounts of uric acid.
Avoid rich foods such as cakes and pies. Leave white flour and sugar products out of your diet.
Avoid the amino acid glycine. Glycine can be converted into uric acid more rapidly in people who suffer from gout.
Limit your intake of caffeine, cauliflower, dried beans, lentils, certain fish, poultry, spinach, and yeast products.
If you are overweight, lose the excess pounds. Losing weight lowers serum uric acid levels. Avoid very restricted weight loss diets (crash diets), however. Abruptly cutting back on foods or fasting for longer than three days may result in increased uric acid levels.
Consider using homeopathic remedies. One helpful homeopathic regimen for gout involves using a combination of Belladonna for severe pain, Arnica for less intense pain, and Rhus toxicodendron for joint pain and itching. Use 3x to 12x strengths and take one doseof each three times each day.
Avoid taking HIGH doses of niacin (over 50 milligrams daily)
Vitamin A in large amounts can exacerbate gout. Make sure you take no more than 5,000 I.U. daily. If you are having attacks, you should stop all vitamin A intake.
Considerations
Gout and gout-like symptoms may be Candida, for it causes uric acid buildup from its waste products.
Some people can have high levels of uric acid with no gout symptoms.
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) is helpful for flare-ups of gout. This oily liquid is applied topically and is reportedly very effective at relieving pain and reducing swelling. Note: Only DMSO from a health food store should be used.
Treatment with honeybee venom has provided relief for some gout sufferers. In this practice, called apitherapy, honeyee venom is administered by injection, either with a hypodermic needle or by the bees themselves. The venom appears to act as both an anti-inflammatory and immune system stimulant.
Deficiencies of certain nutrients can provoke an attack. A deficiency of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) produces excessive amounts of uric acid. A study in animals found that a diet deficient in vitamin A can produce gout. Vitamin E deficiency causes damage to the nuclei of cells that produce uric acid, causing more uric acid to form.
Potassium deficiency is seen in gout. To correct the lack of potassium (the recommended intake is 3,500 mg, but it is safe to take considerably more) take supplements or eat foods high in potassium, such as baked potato, with skin (844), 1 cup cooked spinach (838), ½ cup dried peaches (784), ½ medium avocado (604), 1 cup cantaloupe (494), ½ cup boiled lima beans (478), medium banana (451), 1 cup orange juice (436), 15 raw baby carrots (420), 1 cup of skim milk (406), 1 cup nonfat yogurt (390), ½ cup non-salted tomato sauce (350), 4 oz. lean hamburger (349), ½ cup canned kidney beans (329), yams, dried prunes, etc. If you eat enough of these fruits and vegetables you will not need to take a potassium supplement. Potassium makes the acid crystals go into solution so they can be eliminated.
People who have candida infections, or who have taken antibiotics on and off for long periods, often have increased levels of uric acid in their blood.
Acupressure
Press just below the center of the nose toward the upper lip.
Press and massage between the ball of the foot and the bottom of the big toe on each foot; then on the left foot only, stimulate a point halfway between the base of the little toe and the heel pad.
Press inward and upward on the underside of the protuberance at the base of the skull.
On both hands, press and massage a point on the inside of the pad at the base of the thumb directly beneath the index finger; then on the left palm only, stimulate a point halfway between the base of the little finger and the wrist.
Homeopathy
Tissue salts. To prevent the formation of uric acid crystals, take two tablets of 6X Silicea three times a day. During a gout attack, increase the dosage to three tablets and add an equal amount of Nat. Phos. and Nat. Sulph.
For more specific treatment of symptoms, check out ABCHomeopathy.
Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology (Clin. exp. rheumatol.) ISSN 0392-856X
Abstract
Objective A significant correlation between thyroid function and purine nucleotide metabolism has been established in hypothyroidism. On the contrary, the relationship between hyperthyroidism and purine metabolism is more controversial. The present study evaluates the prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout in patients affected by primary hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Methods. We studied 28 patients with primary hypothyroidism and 18 patients with primary hyperthyroidism, all hospitalized because of endocrine dysfunction. All underwent a series of clinical, biochemical and instrumental evaluations; in particular, thyroid-stimulatin hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (fT4), blood urea, serum creatinine, creatinine clearance, serum and urinary uric acid levels were measured.
Results. In comparison to the prevalence reported in the general population, a significant increase of both hyperuricemia and gout was found in the hypothyroid patients, and of hyperuricemia in the hyperthyroid patients. In hyperthyroidism the hyperuricemia is due to the increased urate production, while in hypothyroidism the hyperuricemia is secondary to a decreased renal plasma flow and impaired glomerular filtration.
Conclusions. Our findings confirm the data in the literature concerning the high prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout in hypothyroidism. It shows that hyperthyroidism can cause a significant increase in serum uric acid, as well, although lower than the hyperuricemia due to thyroid hormone deficiency.
***The connection between hypothyroidism and gout makes it understandable why Lugol's Iodine was used to treat gout in the past.***
It was done by 'painting' the soles of the feet with two drops of Lugol's before retiring for the night allowed the body to absorb what it needed from the soles. If, upon waking, the Lugol's was gone it meant that the body had taken what it needed and needed more. Painting was done on a nightly basis and as treatment progressed, the need for the solution diminished because the body rebuilt its stores and thus absorbed less and less over each 24 hour period until none was absorbed at all.
Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64(12):4004-11 (ISSN: 1529-0131)
Abstract
Objective To study the relationship between cherry intake and the risk of recurrent gout attacks among individuals with gout.
Methods. We conducted a case-crossover study to examine the associations of a set of putative risk factors with recurrent gout attacks. Individuals with gout were prospectively recruited and followed up online for 1 year. Participants were asked to provide the following information regarding gout attacks: the onset date of the gout attack, symptoms and signs, medications (including antigout medications), and exposure to potential risk factors (including daily intake of cherries and cherry extract) during the 2-day period prior to the gout attack. We assessed the same exposure information over 2-day control periods. We estimated the risk of recurrent gout attacks related to cherry intake using conditional logistic regression. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were calculated.
Results. Our study included 633 individuals with gout. Cherry intake over a 2-day period was associated with a 35% lower risk of gout attacks compared with no intake (multivariate OR 0.65 [95% CI 0.50-0.85]). Cherry extract intake showed a similar inverse association (multivariate OR 0.55 [95% CI 0.30-0.98]). The effect of cherry intake persisted across subgroups stratified by sex, obesity status, purine intake, alcohol use, diuretic use, and use of antigout medications. When cherry intake was combined with allopurinol use, the risk of gout attacks was 75% lower than during periods without either exposure (OR 0.25 [95% CI 0.15-0.42]).
Conclusions. These findings suggest that cherry intake is associated with a lower risk of gout attacks.